108. Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree
直接递归
1 | /** |
1 | /** |
1 | /** |
review
1 | /** |
1 | class Solution { |
大的全放后面,小的就留在前面
review
1 | class Solution { |
1 | class Solution { |
每步检查当前的是否符合,如果符合,继承前一个的路数。
当前和前一个叠加的是否符合,如果符合,继承前前的路数
路数是相加的,因为这里分叉了
1 | class Solution { |
review 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20class Solution {
public:
int numDecodings(string s) {
if(s.empty())
return 0;
int n = s.size();
vector<int> dp(n + 1);
dp[0] = 1;
dp[1] = s[0] != '0';
for(int i = 1; i < n; ++i)
{
if(s[i] != '0')
dp[i + 1] += dp[i];
int num = (s[i - 1] - '0') * 10 + (s[i] - '0');
if(10 <= num && num <= 26)
dp[i + 1] += dp[i - 1];
}
return dp.back();
}
};
1 | class Solution { |
O(n)
对于这种方式,由于每行每列都是有序的,所以可以先通过二分查找第一列中最后一个不大于target的数,然后在那一行中二分搜索 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12class Solution {
public:
bool searchMatrix(vector<vector<int>>& matrix, int target) {
auto row = upper_bound(matrix.begin(), matrix.end(), target, [](int a, vector<int>& v){
return a < v[0];
}); // 注意comp是value和容器中的元素比
if(row == matrix.begin())
return false;
--row;
return binary_search(row->begin(), row->end(), target);
}
};
虽然是个二维矩阵,但是每行排开来他就是个递增数列,但是这种方法没有很好的利用他矩阵的特点。
1 | class Solution { |
O(log(m * n))
1 | class Solution { |
对于一个数,截成两段,挨个尝试,每一段由于那个数字在运算时候是不计算他本身的,所以后面用时候需要比较他自己和他break后谁打,所以要有这么多max
discussion 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8You're making it pretty complicated.
If an optimal product contains a factor f >= 4, then you can replace it with factors 2 and f-2 without losing optimality, as 2*(f-2) = 2f-4 >= f. So you never need a factor greater than or equal to 4, meaning you only need factors 1, 2 and 3 (and 1 is of course wasteful and you'd only use it for n=2 and n=3, where it's needed).
For the rest I agree, 3*3 is simply better than 2*2*2, so you'd never use 2 more than twice.
6 = 2 + 2 + 2 = 3 + 3. But 2 * 2 * 2 < 3 * 3.
Therefore, if there are three 2's in the decomposition, we can replace them by two 3's to gain a larger product.
1 | class Solution { |
空间优化 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16class Solution {
public:
int integerBreak(int n) {
vector<int> dp(n + 1);
int a = 0;
int b = 1;
int c = 1;
for(int i = 3; i <= n; ++i)
{
a = max(max(dp[i - 1], max(i - 2, dp[i - 2]) * 2), max(a, i - 3) * 3);
swap(a, b);
swap(b, c);
}
return c;
}
};1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13class Solution {
public:
int integerBreak(int n) {
if(n <= 3)
return n - 1;
int a = n / 3, b = n % 3;
if(b == 1)
return pow(3, a - 1) * 4;
if(b == 2)
return pow(3, a) * 2;
return pow(3, a);
}
};
1 | class NumMatrix { |
大小加一时为了防止下标越界
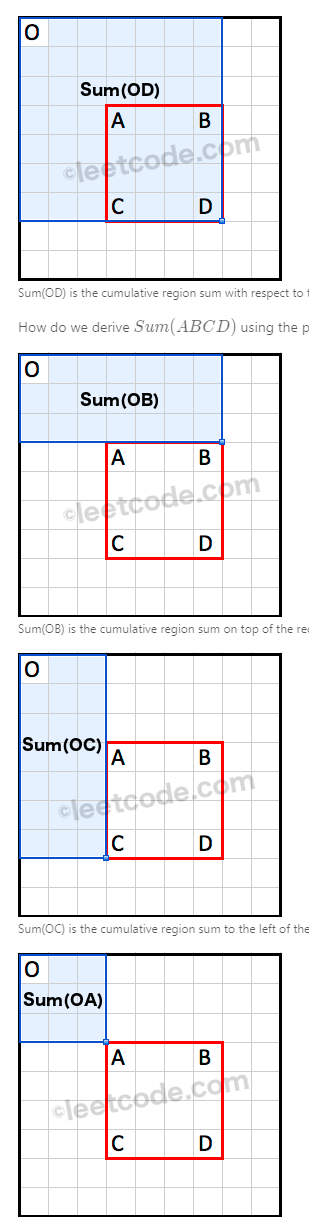
1 | class Solution { |
维护三个序列,分别是x2,x3,x5的序列。其中通过l1,l2,l3表示
这三个序列通过指针的位置来表示,当这个序列的用完后,根据dp中由小到大排,那么移动到下一个作为下一个的候选
之所以可以这样是因为dp已经帮助我们实现排序,因此只需要应用之前的排序结果,取了其中一个序列的一个值后,把他移动到序列的下一个位置,也就是ugly number种刚好比他大的一个数。注意三个数的序列可能会发生重叠。因此需要去重处理。
1 | class Solution { |
因为如果可以实现交替,就必然满足|n - m| <= 1这个条件,所以这个条件可以不用考虑
dp:
1 | class Solution { |
但是在递归过程中,如果有些部分有几个重复的连续串,那么就会产生运算的交叠,所以使用memo来规避已经计算过的内容
sample: 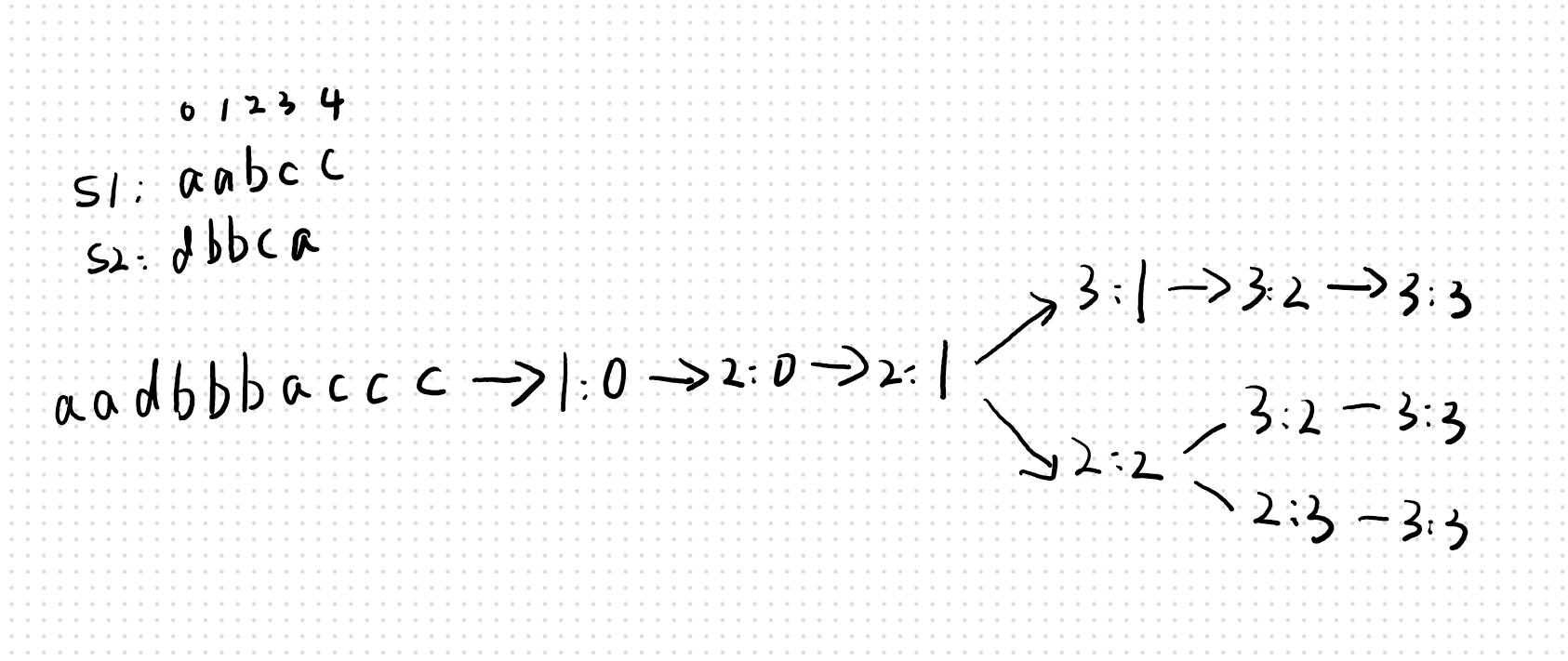
1 | class Solution { |
dp[i][j]表示(0..i)的s1子串和(0..j)的s2子串,如果他们可以交错成一个(0...i+j+1)的s3子串,那么就是true
2种情况
s1[i]!=s3[i+j+1] && s2[j]!=s3[i+j+1],那么绝对为false,因为某尾匹配不了s1[i]==s3[i+j+1]时,那么结果等同于dp[i-1][j],最后一位把s1[i]匹配走了,那么如果之前都匹配成功,就是true了,当s2[j]==s3[i+j+1]时同理base:
当一个子串为空串时候的匹配结果
1 | class Solution { |
优化空间
1 | class Solution { |
review
1 | class Solution { |