543. Diameter of Binary Tree
遍历
1 | /** |
顺路计算完所有的点
1 | /** |
1 | /** |
1 | /** |
1 | class Solution { |
T(n) : O(nlogn)
1 | class Solution { |
1 | class Solution { |
T(n) : O(nlogn)
S(n) : O(n)
1 | class Solution { |
最好的情况下时只进行一次partition, 为O(n)
最坏的情况是对于每个元素都进行partition 为O(n^2)
将原数组进行洗牌后可以保证O(n)
1 | class Solution { |
深度优先遍历,当遇到一块陆地后,向周围遍历,遍历过的土地做上标记防止重复遍历,当遍历完一整块岛后,返回,计数加一
对discuss中的代码加以批注
1 | int[][] distance = {{1,0},{-1,0},{0,1},{0,-1}}; // 4个方向 |
Union Find:
1 | class UnionFind { |
1 | class Solution { |
1 | class Solution { |
1 | class Solution { |
当负数的个数为偶数时,全乘起来就是最大,为奇数时,需要抛弃一个
每次的乘法,最大的乘积受到最后一个负数的限制
review
当负数个数为偶数且中间没有0,那么无论左到右还是右到左都会遍历到。
抛开此外,可以观察到分界线为0,每一块被0分开的没0区域都表示一个乘积,当这一个区域没有负数或者负数个数为偶数,那么无论左到右还是右到左都会遍历到。当为奇数,那么以其中一个负数为分界线将分成左右2块为偶的区域,由此需要左到右和右到左遍历。
1 | class Solution { |
使用原数列中的坐标是否为负来表征当前坐标所代表的值是否存在。由此使得S(n) = O(n)
聪明啊!
1 | class Solution { |
1 | class Solution { |
1 | class Solution { |
1 | /** |
1 | /** |
1 | /** |
他们第一次跑会有一个长度的差,短的先跑到终点后,到长的端点。当长的指针跑到终点后,回到短的端点。此时先前一个刚好跑了他们的距离差,这是他们在距离上是处于同一个起点的。
设短的到交点距离x,长的到交点距离y,公共部分距离为z,则如果要求交点,那么让他们走到交点的路程一致即可,则让短的走到头后跳到长,长的走到头后跳到短,最后对于短头来说x+y+z,长头也是x+y+z,刚好在交点相交。
review
如果没交点,第二轮时候他们肯定一同走到尾巴。长的比短的多出来的步数,由于短的先走到头,然后比长的走到短头会刚好多走这么几步,于是就处于同意起跑线。
具体见discussion中的评论第一条
1 | /** |
T(n) : O(n)
S(n) : O(n)
1 | /** |
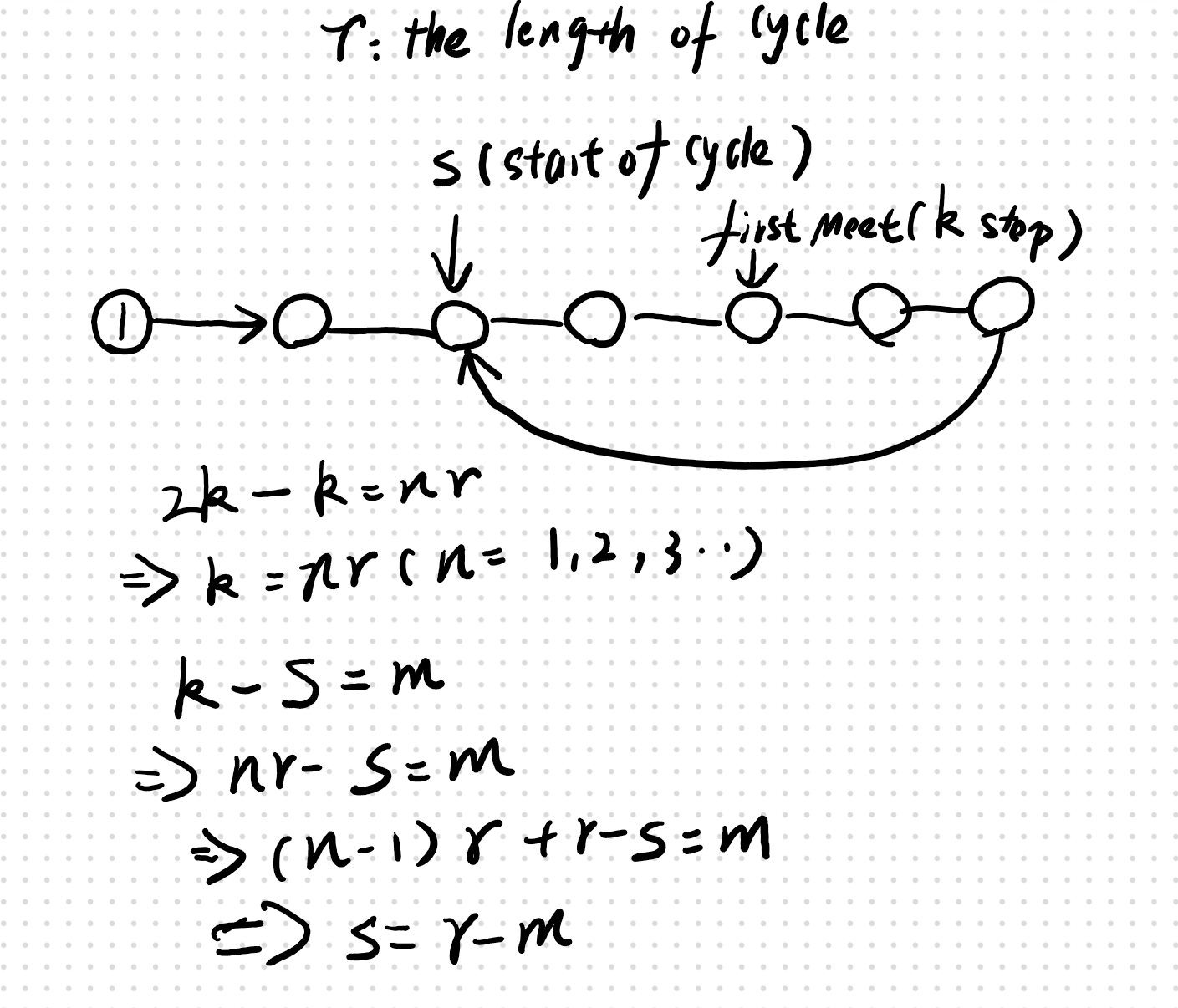 即当一个点从第一次遇见的点开始,走r-m步,走到环的起始点时,另一个点刚好从起点走到环的起始点
即当一个点从第一次遇见的点开始,走r-m步,走到环的起始点时,另一个点刚好从起点走到环的起始点
针对最后取为1的修订 1
Smart solution. But replacing all "wake" to "walk" in your words makes me feel better :) Another minor point is you can't just "here we takes n = 1" even it doesn't affect the last result. It still should read as s=nr-m. That means the 1st pointer starts from beginning of the list while the 2nd pointer starts from meet point, they will meet in the cycle point but the 2nd pointer walked n times of the cycle.
r2-2r1(设为n)圈,这个数字为正即可,因为不管他多走几圈都影响不了结果。而r2是runner走的圈数,r1是walker走的圈数。
k为步数,s为起点到环起点的距离,m为圈长 r2 = (2k - s) / m,而r1 = (k - s) / m,则r2 / r1 = 2 + s/k+s,所以r2 - 2r1 = s / k + s必定为正数
太难了
1 | /** |
每个在preorder中的点在inorder中的左边都是左树,右边是右树
The two key observations are:
Preorder traversal follows Root -> Left -> Right, therefore, given the preorder array preorder, we have easy access to the root which is preorder[0].
Inorder traversal follows Left -> Root -> Right, therefore if we know the position of Root, we can recursively split the entire array into two subtrees.
1 | /** |
还有使用递归,传入层数,对每一层的vector容器加入
review 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root)
return {};
vector<vector<int>> ret;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty())
{
ret.emplace_back();
for(int i = 0, sz = q.size(); i < sz; ++i)
{
auto p = q.front();
q.pop();
ret.back().push_back(p->val);
if(p->left)
q.push(p->left);
if(p->right)
q.push(p->right);
}
}
return ret;
}
};
1 | /** |
1 | /** |
1 | /** |