8. String to Integer (atoi)
第一次
1 | class Solution |
坑有点多,起初忽视了很多种情况
其中判断是否溢出参考了https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-integer/solution/
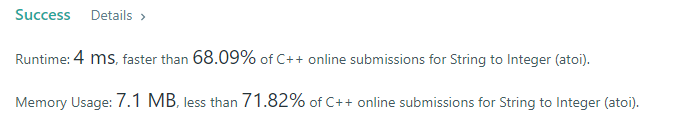
1 | class Solution |
坑有点多,起初忽视了很多种情况
其中判断是否溢出参考了https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-integer/solution/

1 | class Solution |
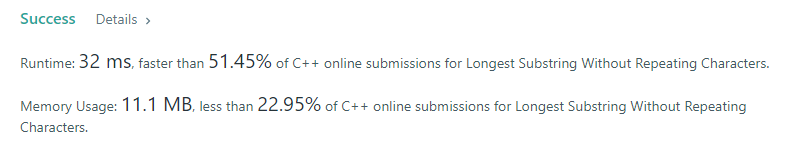
sliding window 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
unordered_map<char, int> memo;
int begin = 0, end = 0, sz = s.size();
int ret = 0;
while(end < sz)
{
char ch = s[end++];
++memo[ch];
while(memo[ch] > 1)
--memo[s[begin++]];
ret = max(ret, end - begin);
}
return ret;
}
};1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
unordered_set<char> memo;
int begin = 0, end = 0, sz = s.size();
int ret = 0;
while(end < sz)
{
char ch = s[end++];
while(memo.count(ch))
memo.erase(s[begin++]);
memo.emplace(ch);
ret = max(ret, end - begin);
}
return ret;
}
};1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
vector<int> memo(256, -1);
int begin = -1, end = 0, ret = 0;
int sz = s.size();
for(; end < sz; ++end)
{
begin = max(begin, memo[s[end]]); // 如果当前的字符在[begin, end]区域重复了,就把begin移动到前一个s[end]出现的地方,跳跃
memo[s[end]] = end; // 更新当前字符最后出现的坐标
ret = max(ret, end - begin);
}
return ret;
}
};1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLongestSubstring(string s) {
unordered_map<char, int> memo;
int begin = 0, end = 0, ret = 0;
int sz = s.size();
for(; end < sz; ++end)
{
begin = max(begin, memo[s[end]]);
memo[s[end]] = end + 1; // map中默认初始化为0,所以这里加以改变
ret = max(ret, end - begin + 1);
}
return ret;
}
};
1 | class Solution |
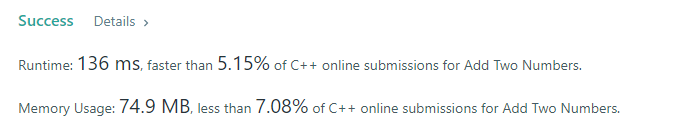
1 | class Solution { |